Applications
400G OSFP-RHS LR4 10Km EML Transceiver Module
ROSP-RHS-400G-LR4C
Description
This FIBERWDM ROSP-RHS-400G-LR4C product is designed for 10km optical communication applications. The module converts 4 channels of 100Gb/s (PAM4) electrical input data to 4 channels of CWDM optical signals, and multiplexes them into a single channel for 400Gb/s optical transmission. Reversely, on the receiver side, the module optically de-multiplexes a 400Gb/s optical input into 4 channels of CWDM optical signals and converts them to 4 channels of 100Gb/s (PAM4) electrical output data.
The module incorporates 4 independent channels on CWDM4 1271/1291/1311/1331nm center wavelength, operating at 100G per channel. The transmitter path incorporates 4 independent EML drivers and EML lasers together with an optical multiplexer. On the receiver path, an optical de- multiplexer is coupled to a 4-channel photodiode array.
It is a cost-effective and lower power consumption solution for 400GBASE data center. It has been designed to meet the harshest external operating conditions including temperature, humidity and EMI interference. The module offers very high functionality and feature integration, accessible via a two-wire serial interface.
Features
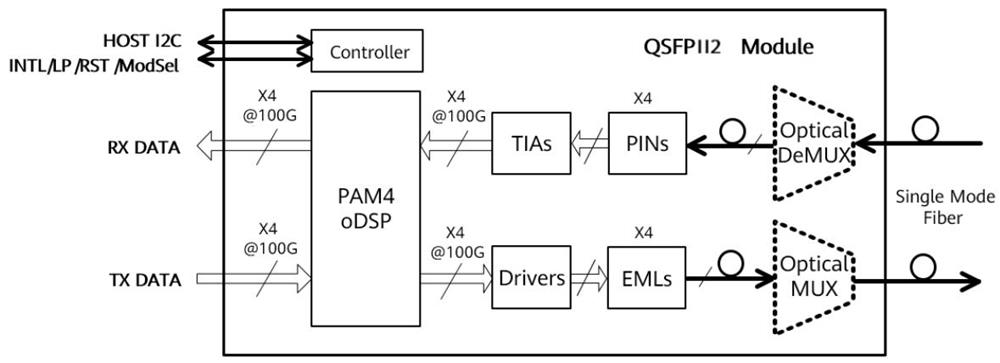
Figure1. Module Block Diagram
Absolute Maximum Ratings
| Parameter | Symbol | Min | Max | Unit |
| Supply Voltage | Vcc | -0.3 | 3.6 | V |
| Input Voltage | Vin | -0.3 | Vcc+0.3 | V |
| Storage Temperature | Tst | -40 | 85 | ºC |
| Case Operating Temperature | Top | 0 | 70 | ºC |
| Humidity(non-condensing) | Rh | 5 | 95 | % |
Recommended Operating Conditions
| Parameter | Symbol | Min | Typical | Max | Unit |
| Supply Voltage | Vcc | 3.13 | 3.3 | 3.47 | V |
| Operating Case temperature | Tca | 0 | 70 | ºC | |
| Data Rate Per Lane | fd | 106.25 | Gbit/s | ||
| Humidity | Rh | 15 | 85 | % | |
| Power Dissipation | Pm | 10 | W |
Electrical Specifications
| Parameter | Symbol | Min | Typical | Max | Unit |
| Differential input impedance | Zin | 90 | 100 | 110 | ohm |
| Differential Output impedance | Zout | 90 | 100 | 110 | ohm |
| Differential input voltage amplitude | ΔVin | 900 | mVp-p | ||
| Differential output voltage amplitude | ΔVout | 900 | mVp-p | ||
| Bit Error Rate | BER | 2.4E-4 | |||
| Near-end ESMW (Eye symmetry mask width) | 0.265 | UI | |||
| Near-end Eye height, differential (min) | 70 | mV | |||
| Far-end ESMW (Eye symmetry mask width) | 0.20 | UI | |||
| Far-end Eye height, differential (min) | 30 | mV | |||
| Far-end pre-cursor ISI ratio | -4.5 | 2.5 | % |
Note:
1) BER=2.4E-4; PRBS31Q@53.125GBd. Pre-FEC
2) Differential input voltage amplitude is measured between TxnP and TxnN.
3) Differential output voltage amplitude is measured between RxnP and RxnN.
Optical Characteristics
Table 3 - Optical Characteristics
| Parameter | Symbol | Min | Typical | Max | Unit | Notes |
| Transmitter | ||||||
| Centre Wavelength | λ0 | 1264.5 | 1271 | 1277.5 | nm | |
| λ1 | 1284.5 | 1291 | 1297.5 | nm | ||
| λ2 | 1304.5 | 1311 | 1317.5 | nm | ||
| λ3 | 1324.5 | 1331 | 1337.5 | nm | ||
| Side-mode suppression ratio | SMSR | 30 | dB | |||
| Average launch power, each lane | Pout | -2.7 | 5.1 | dBm | ||
| Optical Modulation Amplitude(OMA outer), each lane | OMA | 0.3 | 4.4 | dBm | ||
| Transmitter and dispersion eye closure for PAM4 (TDECQ),each lane | TDECQ | 3.9 | dB | |||
| Extinction Ratio | ER | 3.5 | dB | |||
| Average launch power of OFF transmitter, each lane | -16 | dB | ||||
| Receiver | ||||||
| Centre Wavelength | λ0 | 1264.5 | 1271 | 1277.5 | nm | |
| λ1 | 1284.5 | 1291 | 1297.5 | nm | ||
| λ2 | 1304.5 | 1311 | 1317.5 | nm | ||
| λ3 | 1324.5 | 1331 | 1337.5 | nm | ||
| Receiver Sensitivity in OMA outer | RXsen | -6.8 | dBm | 1 | ||
|
Average power at receiver , each lane input, each lane |
Pin | -9 | 5.1 | dBm | ||
| Receiver Reflectance | -26 | dB | ||||
| LOS Assert | -12 | dBm | ||||
| LOS De-Assert | -10 | dBm | ||||
| LOS Hysteresis | 0.5 | dB | ||||
Note:
1) Measured with conformance test signal at TP3 for BER = 2.4E-4 Pre-FEC
Pin Description
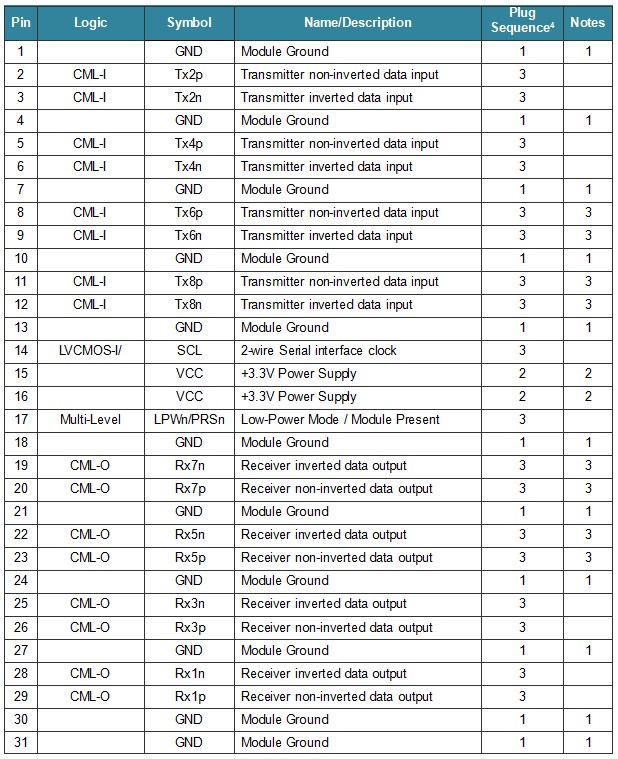
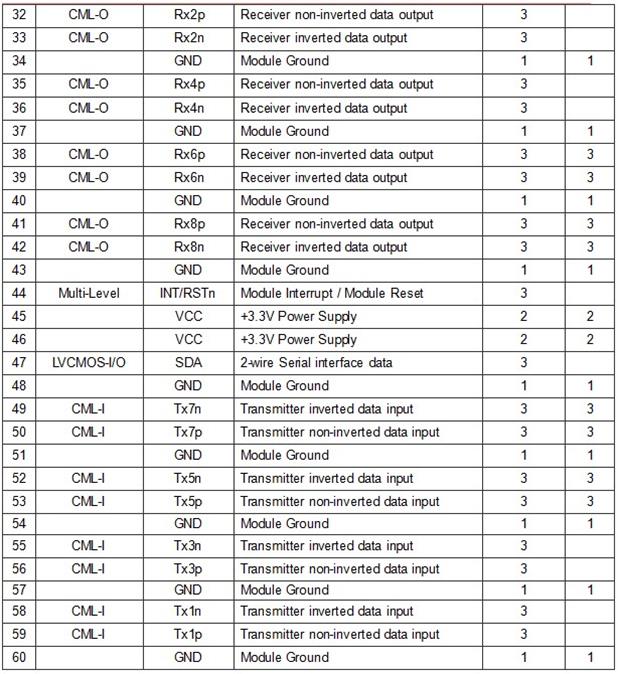
Note:
1): GND is the symbol for signal and supply (power) common for the OSFP-RHS module. All are common within the OSFP-RHS module and all voltages are referenced to this potential unless otherwise noted. Connect these directly to the host board signal-common ground plane.
2): VCC are the OSFP-RHS power supplies and shall be applied concurrently. The connector pins are each rated for a maximum current of 1.5A (max. current of 2.0 A is required for high module power of 15-20W).
3): Not connected in OSFP-RHS.
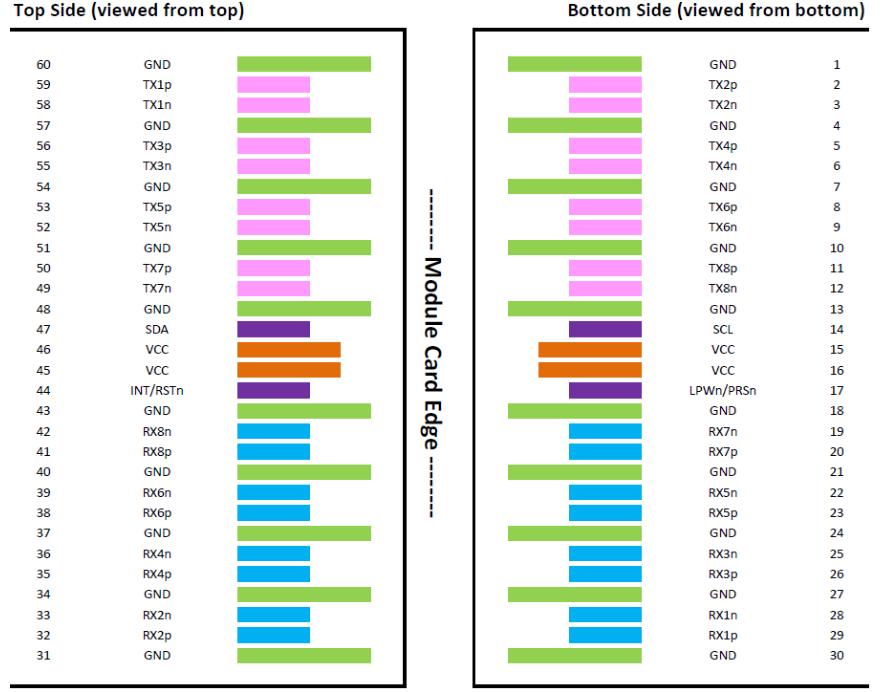
Figure2. OSFP-RHS Module contact assignment
INT/RSTn Pin
INT/RSTn is a dual function signal that allows the module to raise an interrupt to the host,and also allows the host to reset the module. The circuit shown in Figure 3 enables multi-level signaling to provide direct signal control in both directions. Reset is an active-low signal on the host which is translated to an active-low signal on the module. Interrupt is an active-high signal on the module which gets translated to an active-high signal on the host.The INT/RSTn signal operates in 3 voltage zones to indicate the state of Reset for the module and Interrupt for the host.
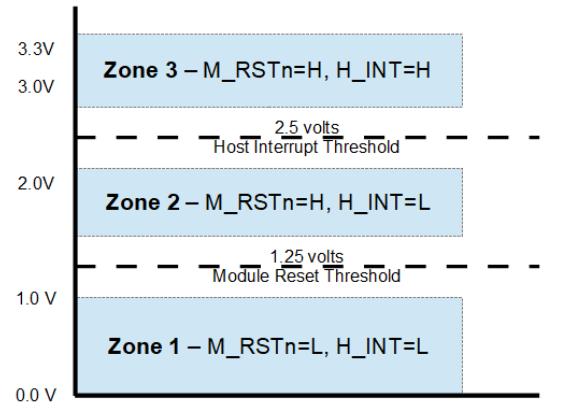
Figure 3. INT/RSTn voltage zones
LPWn/PRSn Pin
LPWn/PRSn is a dual function signal that allows the host to signal Low Power mode and the module to indicate Module Present. The circuit shown in Figure 4 enables multi-level signaling to provide direct signal control in both directions. Low Power mode is an active-low signal on the host which gets converted to an active-low signal on the module. Module Present is controlled by a pull-down resistor on the module which gets converted to an active-low logic signal on the host.
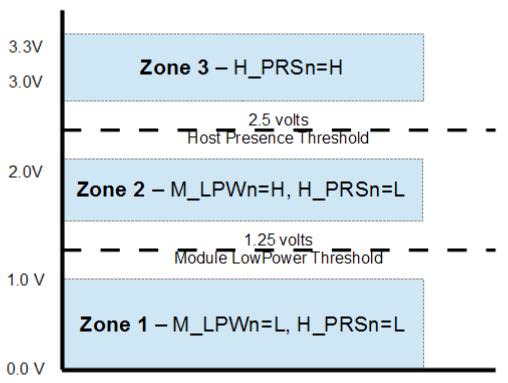
Figure 4. LPWn/PRSn voltage zones
OSFP Host Board and Module Block Diagram
Figure 5 is an example block diagram of the host board’s connections to the OSFP module.
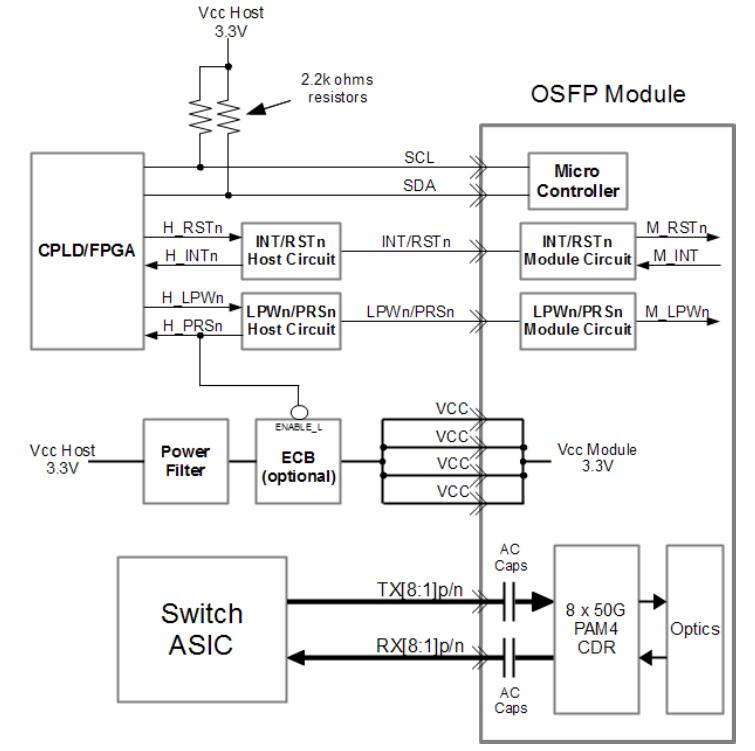
Figure5. Host board and Module block diagram
DIAGNOSTIC MONITORING INTERFACE
Digital diagnostics monitoring function is available on all FIBERWDM OSFP-RHS products. A 2-wire serial interface provides user to contact with module.
Memory Structure and Mapping
This limits the management memory that can be directly accessed by the host to 256 bytes, which is divided in Lower Memory (addresses 00h through 7Fh) and Upper Memory (addresses 80h through FFh).
A larger addressable management memory is required for all but the most basic modules. This is supported by a structure of 128-byte pages, together with a mechanism for dynamically mapping any of the 128-byte pages from a larger internal management memory space into Upper Memory the host addressable space.
The addressing structure of the additional internal management memory2 is shown in Figure 4 The management memory inside the module is arranged as a unique and always host accessible address space of 128 bytes (Lower Memory) and as multiple upper address subspaces of 128 bytes each (Pages), only one of which is selected as host visible in Upper Memory. A second level of Page selection is possible for Pages for which several instances exist (e.g. where a bank of pages with the same Page number exists).
This structure supports a flat 256 byte memory for passive copper modules and permits timely access to addresses in the Lower Memory, e.g. Flags and Monitors. Less time critical entries, e.g. serial ID information and threshold settings, are available with the Page Select function in the Lower Page. For more complex modules which require a larger amount of management memory the host needs to use dynamic mapping of the various Pages into the host addressable Upper Memory address space, whenever needed.
Note: The management memory map has been designed largely after the QSFP memory map. This memory map has been changed in order to accommodate 8 electrical lanes and to limit the required memory space. The single address approach is used as found in QSFP. Paging is used in order to enable time critical interactions between host and module.
Supported Pages
A basic 256 byte subset of the Management Memory Map is mandatory for all CMIS compliant devices. Other parts are only available for paged memory modules, or when advertised by the module. See CMIS V4.0 for details regarding the advertisement of supported management memory spaces.
In particular, support of the Lower Memory and of Page 00h is required for all modules, including passive copper cables. These pages are therefore always implemented. Additional support for Pages 01h, 02h and bank 0 of Pages 10h and 11h is required for all paged memory modules.
Bank 0 of pages 10h-1Fh, provides lane-specific registers for the first 8 lanes, and each additional bank provides support for additional 8 lanes. Note, however, that the allocation of information over the banks may be page specific and may not to be related to grouping data for 8 lanes.
The structure allows address space expansion for certain types of modules by allocating additional Pages. Moreover, additional banks of pages.
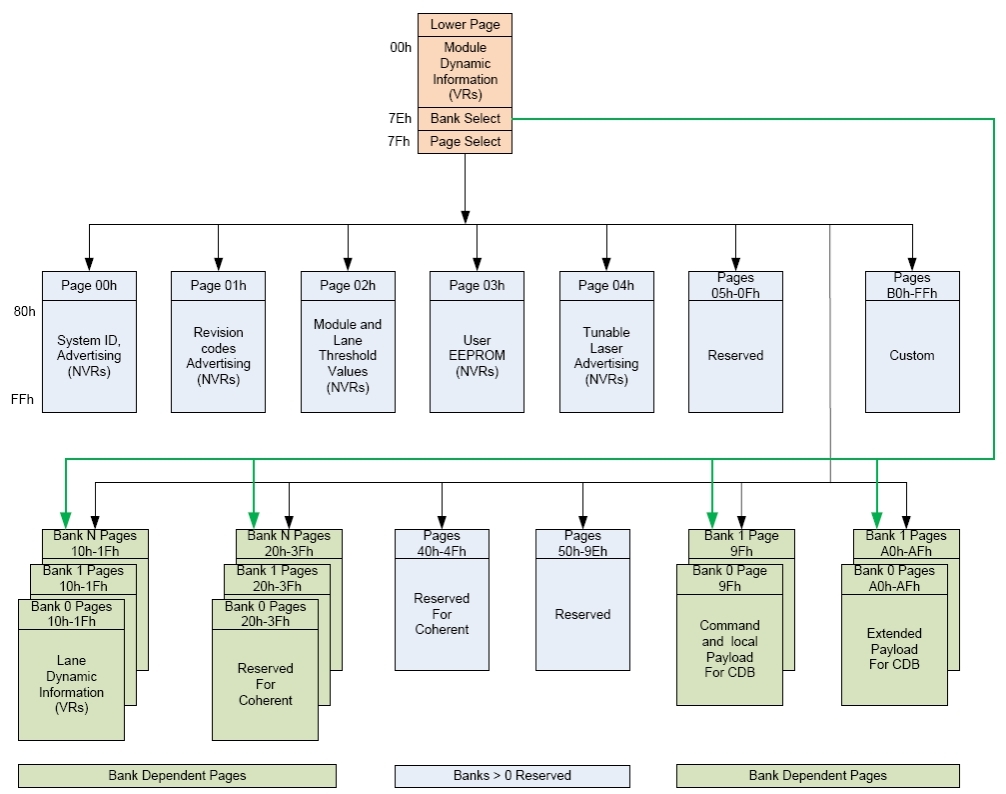
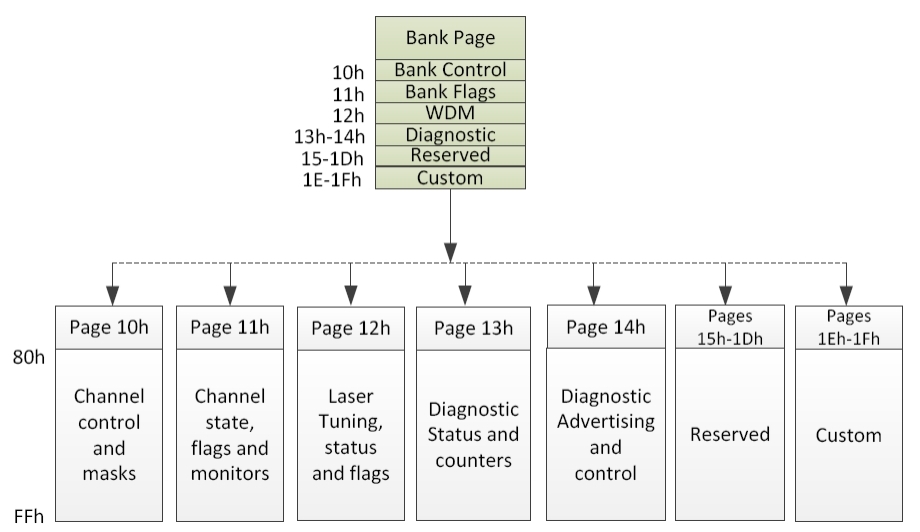
Figure4. QSFP112 Memory Map
Mechanical Dimensions
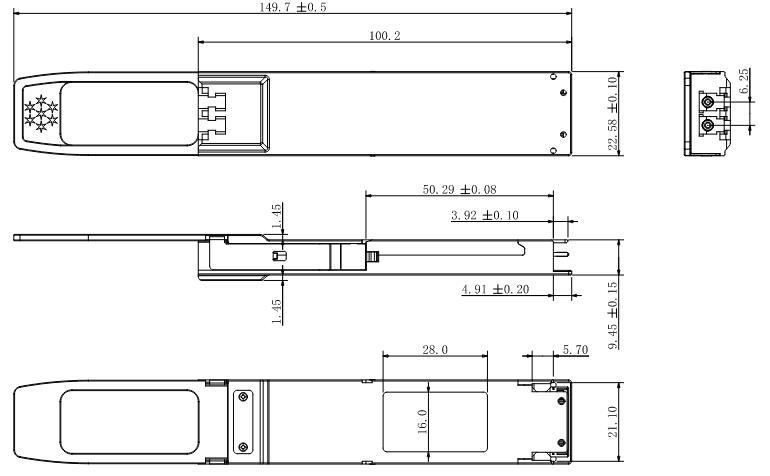
Figure5. Mechanical Specifications
Regulatory Compliance
FIBERWDM ROSP-RHS-400G-LR4C transceivers are Class 1 Laser Products. They meet the requirements of the following standards:
| Feature | Standard |
| Laser Safety |
IEC 60825-1:2014 (3rd Edition) EN 60825-2:2004+A1+A2 |
| Electrical Safety |
EN 62368-1: 2014 IEC 62368-1:2014 UL 62368-1:2014 |
| Environmental protection | Directive 2011/65/EU with amendment(EU)2015/863 |
| CE EMC | EN55032:2015 EN55035:2017 EN61000-3-2:2014 EN61000-3-3:2013 |
| FCC |
FCC Part 15, Subpart B ANSI C63.4-2014 |
References
1. OSFP MSA
2. CMIS 4.0
3. 400G-LR4 Technical Specification
4. IEEE802.3ck
5. OIF CEI-112G-VSR-PAM4
CAUTION:
Use of controls or adjustment or performance of procedures other than those specified herein may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
Ordering information
| Part Number | Product Description |
| ROSP-RHS-400G-LR4C | OSFP-RHS, 400GBASE-LR4, 10Km on Single mode Fiber (SMF),with DSP Power consumption <10W, duplex LC connector. |
Important Notice
Performance figures, data and any illustrative material provided in this data sheet are typical and must be specifically confirmed in writing by FIBERWDM before they become applicable to any particular order or contract. In accordance with the FIBERWDM policy of continuous improvement specifications may change without notice.
The publication of information in this data sheet does not imply freedom from patent or other protective rights of FIBERWDM or others. Further details are available from any FIBERWDM sales representative.
Want to know about this product?
If you are interested in our products and want to know more details,please leave a message here,we will reply you as soon as we can.